1.11 为什么使用卷积?(Why convolutions?)
和只用全连接层相比,卷积层的两个主要优势在于参数共享和稀疏连接
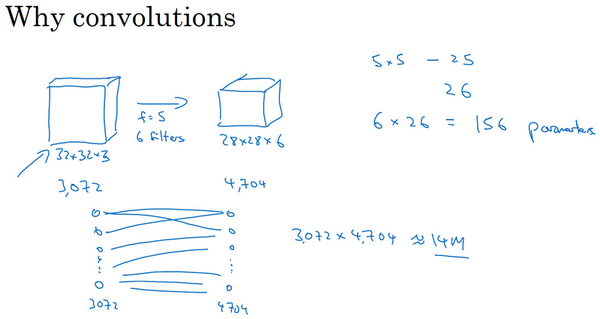
如果这是一张1000×1000的图片,权重矩阵会变得非常大。而卷积层的参数数量:每个过滤器都是5×5,一个过滤器有25个参数,再加上偏差参数,那么每个过滤器就有26个参数,一共有6个过滤器,所以参数共计156个,参数数量很少
卷积网络映射这么少参数有两个原因:
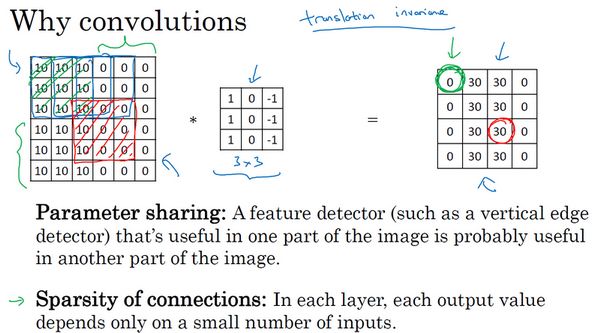
参数共享:一个特征检测器(例如垂直边缘检测)对图片某块区域有用,同时也可能作用在图片其它区域。
特征检测如垂直边缘检测如果适用于图片的某个区域,那么它也可能适用于图片的其他区域。如果用一个3×3的过滤器检测垂直边缘,那么图片的左上角区域,以及旁边的各个区域(左边矩阵中蓝色方框标记的部分)都可以使用这个3×3的过滤器。每个特征检测器以及输出都可以在输入图片的不同区域中使用同样的参数,以便提取垂直边缘或其它特征。它不仅适用于边缘特征这样的低阶特征,同样适用于高阶特征,例如提取脸上的眼睛,猫或者其他特征对象。即使减少参数个数,这9个参数同样能计算出16个输出。直观感觉是,一个特征检测器,如垂直边缘检测器用于检测图片左上角区域的特征,这个特征很可能也适用于图片的右下角区域。因此在计算图片左上角和右下角区域时,不需要添加其它特征检测器
连接的稀疏性:因为滤波器算子尺寸限制,每一层的每个输出只与输入部分区域内有关
右边输出单元(元素0)仅与36个输入特征中9个相连接。其它像素值都不会对输出产生任何影响,输出(右边矩阵中红色标记的元素 30)仅仅依赖于这9个特征(左边矩阵红色方框标记的区域),只有这9个输入特征与输出相连接,其它像素对输出没有任何影响
神经网络可以通过这两种机制减少参数,以便用更小的训练集来训练它,从而预防过拟合。CNN比较擅长捕捉区域位置偏移,也就是说CNN进行物体检测时,不太受物体所处图片位置的影响,增加检测的准确性和系统的健壮性。通过观察可以发现,向右移动两个像素,图片中的猫依然清晰可见,因为神经网络的卷积结构使得即使移动几个像素,这张图片依然具有非常相似的特征,应该属于同样的输出标记
最后,把这些层整合起来,比如要构建一个猫咪检测器,x表示一张图片,y^是二进制标记或某个重要标记。选定一个卷积神经网络,输入图片,增加卷积层和池化层,然后添加全连接层,并随机初始化参数w和b,最后输出一个softmax,即y^,代价函数J等于神经网络对整个训练集的预测的损失总和再除以m(即CostJ=m1∑i=1mL(y^(i),y(i)))。所以训练神经网络,要做的就是使用梯度下降法,或其它算法,例如Momentum梯度下降法,含RMSProp或其它因子的梯度下降来优化神经网络中所有参数,以减少代价函数J的值
Last updated